Are you experiencing mood changes? Is your weight fluctuating, but you can’t figure out why?
These could be due to issues with your thyroid. The team at Maryland ENT is here to help treat these concerns and get you back to feeling your best.
What is a Thyroid?
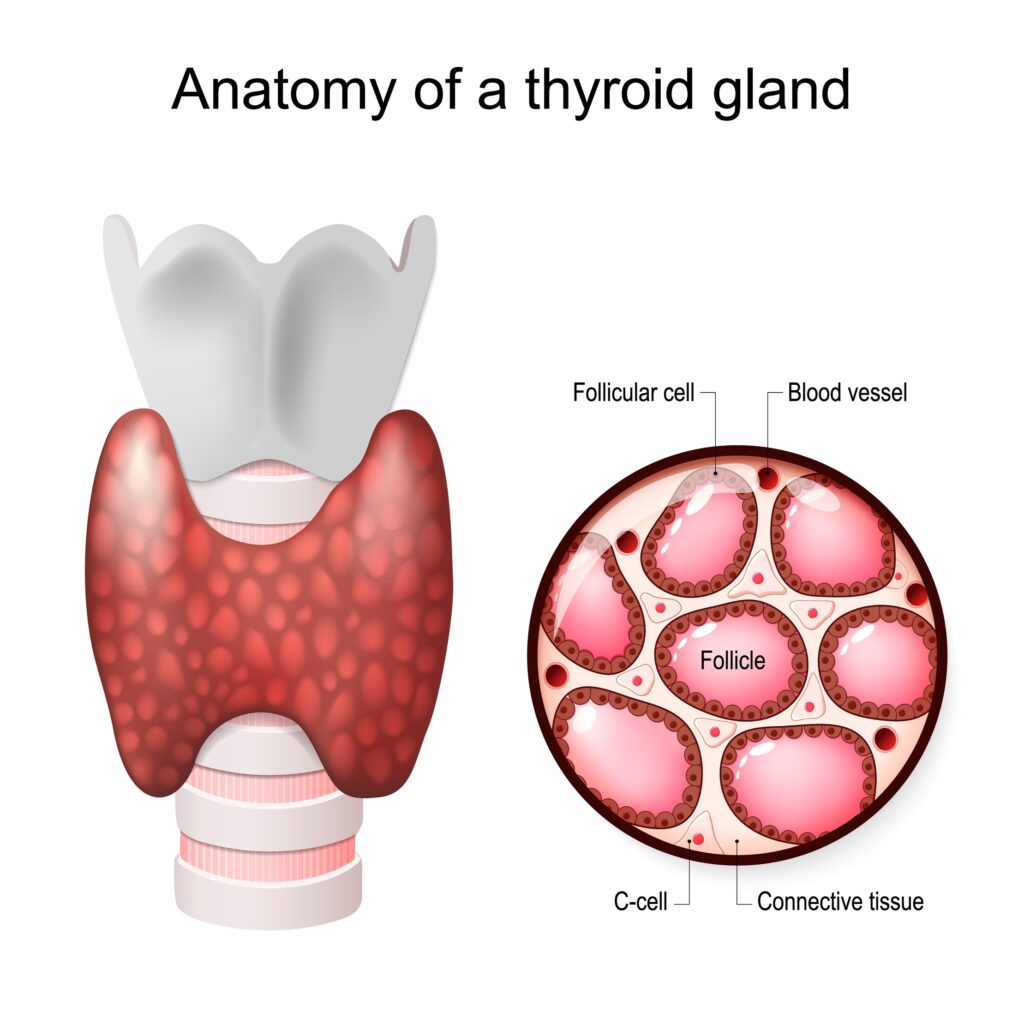
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland in the front of your neck, just below your “Adam’s apple.” It comprises two lobes: the left lobe and the right lobe. You can think of them as the left and right butterfly wings.
The thyroid’s main job is to make and release hormones that regulate metabolism. Metabolism refers to how your entire body uses energy, so when the thyroid is faulty, it can affect your whole body and overall well-being.
How Does the Thyroid Work?
The thyroid is a part of the endocrine system. The endocrine system contains multiple glands that make and release hormones into the bloodstream.
Hormones are carried from where they are made throughout the rest of the body through the bloodstream. They are chemicals that bring a message to different organs of your body, letting it know what to do and when to do it.
The thyroid makes and releases hormones that tell the body how and when to metabolize or use energy. Metabolism is vital for regulating temperature, converting food to energy, thinking clearly and being alert, and keeping the brain, heart, lungs, muscles, reproductive system, and other organs working efficiently.
Symptoms of Thyroid Issues
Because the thyroid is necessary for communicating messages to the entire body through hormones, a problem with your thyroid could impact many different systems of your body. If you have a concern or new symptoms, talk to your doctor at Maryland ENT. You can always ask if it might be related to your thyroid.
Some common symptoms of problems with the thyroid are:

- Unintentional weight gain or weight loss
- Depression or anxiety
- Other mood changes
- Difficulty keeping a stable body temperature
- Extra sensitivity to heat and cold
- Slow or rapid heart rate
- Irregular menstrual periods
- Pain in the neck or throat
- Chronic coughing or throat-clearing
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Voice or swallowing changes
What are Some Common Thyroid Problems?
Thyroid disease is a very common diagnosis, and it refers to any problem with your thyroid. Women are significantly more likely than men to experience thyroid disease.
The four ways that thyroid disease presents are hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, goiter, and thyroid cancer.
Hypothyroidism is when your thyroid is underperforming; it does not produce or release enough hormones to keep your metabolism going as it should. This causes your metabolism to slow, leading to fatigue, weight gain, slowed heart rate, depression, and more. You can treat hypothyroidism with medication.
Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid overachieves. The thyroid makes and releases more hormones than the body needs.
This kicks the metabolism into high gear, leading to weakness and fatigue, unexpected weight loss, anxiety, difficulty sleeping, an irregular heart rate, a racing heart, and swelling in the neck. Hyperthyroidism can also be treated with medication.
Goiter is an enlargement of the thyroid gland; it is usually seen or felt as a swelling or lump protruding from the front of the neck, just below or around the Adam’s apple.
Thyroid cancer refers to cancer that originates in the thyroid gland. Treatment for thyroid cancer has a high success rate and may involve surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation.
If you have any concerns about your thyroid or any symptoms related to it, your doctor at Maryland ENT may recommend a blood test that checks the levels of the thyroid hormones. If the thyroid is enlarged or there is a bump or mass on it (a “nodule”), your ENT specialist may recommend a biopsy to find out more about the nature of the nodule.
Usually, your ENT specialist will recommend a “fine needle aspiration biopsy” first. This procedure involves using a needle to draw out fluid, which is then sent to a lab and analyzed.
If your ENT specialist determines that more information is needed, you may have an “excisional biopsy,” which involves surgically removing part of the lump and then sending it to the lab to be analyzed for more information.
Why Would I Need Thyroid Surgery?

If your fine needle aspiration biopsy of the thyroid nodule or other growth shows that you have cancer or possible cancer, or the biopsy was inconclusive, your ENT specialist will likely recommend thyroid surgery to remove part or all of your thyroid. You won’t need every thyroid nodule removed; if the biopsy shows that it is benign or harmless, it does not need to be surgically removed.
However, if the biopsy shows that the growth is cancerous or if the results are inconclusive, it must be surgically removed and biopsied further. Sometimes, it is recommended that the entire thyroid be removed.
It is possible to live without a thyroid; however, if your thyroid is removed, you will need to take hormone replacements to replace the hormones made in the thyroid.
Sometimes, medication or hormone replacement is recommended whether or not you have surgery. Your ENT specialist will provide education and information about the best way to treat your thyroid problem.
Minimally Invasive Thyroid Surgery
If you must have thyroid surgery to remove all or part of your thyroid, there are now options for minimally invasive thyroid surgery, which decreases the appearance of scarring. The surgical incisions are camouflaged within your natural skin creases in your neck, making surgical scarring less noticeable.
This new technique is also highly beneficial in protecting two vital nerves located near the thyroid; damage to these nerves is a risk of any traditional neck or chest surgery, but the risk is decreased with the minimally invasive surgical method. Ask your doctor at Maryland ENT if minimally invasive thyroid surgery is right for you.
Do you suspect you could have a thyroid problem? Get the answers to your questions by scheduling an appointment at Maryland ENT in Lutherville and Baltimore, MD, now!



